In today’s health-conscious world, terms like overweight and obesity are frequently used, often interchangeably, but they refer to distinct conditions with different health implications. Both conditions relate to excess body weight, but the degree and potential health risks associated with each differ. Understanding the difference between being overweight and obese can help individuals better manage their health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Welcome to the
Obesity
Community
Welcome to our journal. Here you can find the latest Clinical Trials insights and articles.
Join Upcoming Event
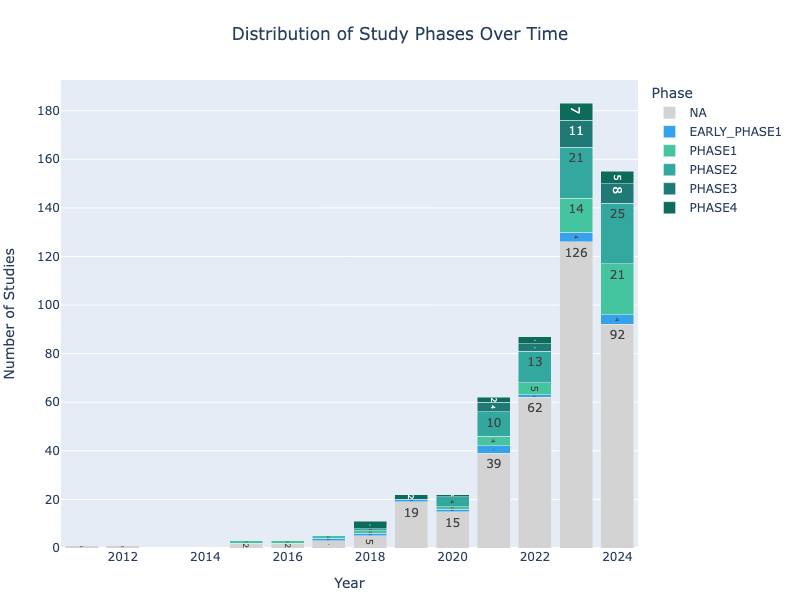
Obesity is indeed classified as a chronic medical condition, meaning it persists over a long period of time and requires ongoing management. It is not simply a matter of temporary weight gain but involves a complex interaction of genetic, behavioral, environmental, and metabolic factors that lead to excessive fat accumulation. Obesity is associated with a range of serious health complications, including diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers, and managing it often requires long-term lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and support.
Obesity is a complex, chronic condition that goes beyond just excess weight. Treating obesity involves not only addressing physical aspects but also the psychological, behavioral, and environmental factors that contribute to it. Managing obesity as a chronic condition presents unique challenges, particularly because it requires long-term commitment, individualized care, and ongoing support.
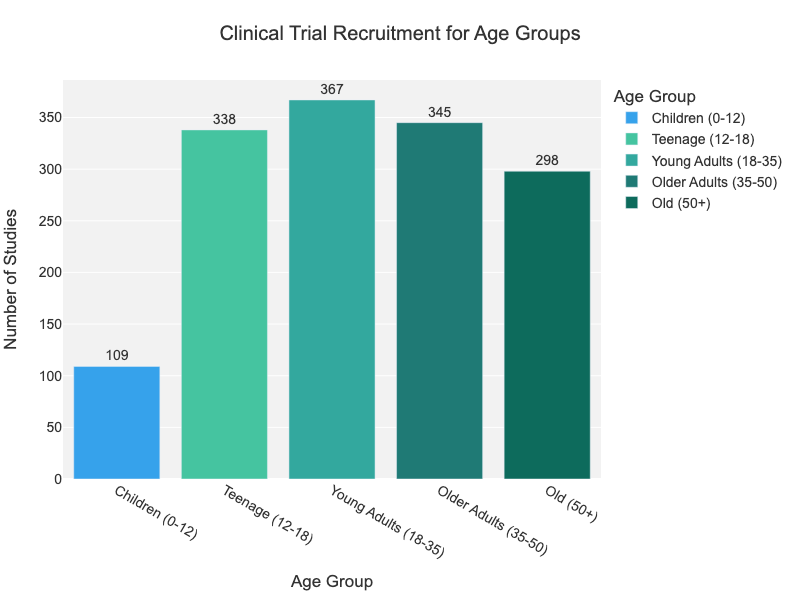
While it might seem counterintuitive, individuals with obesity can often suffer from nutritional deficiencies. Despite having excess body fat, many people with obesity do not consume the essential nutrients needed to maintain overall health. This is largely due to the consumption of calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods and poor dietary habits that prioritize processed and fast foods over fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-rich options.
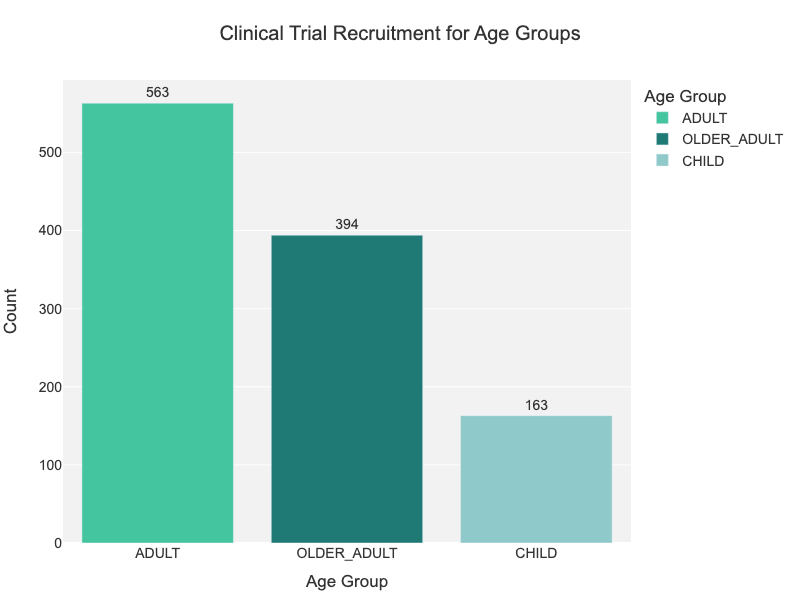
Obesity is a complex, chronic condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach for effective management. While primary care physicians (PCPs) are often the first point of contact for patients with obesity, there is ongoing debate about whether they are sufficiently trained to address the multifaceted needs of individuals struggling with excess weight. Many PCPs feel underprepared or lack the necessary resources and time to provide comprehensive care for obesity, despite the growing prevalence of the condition.
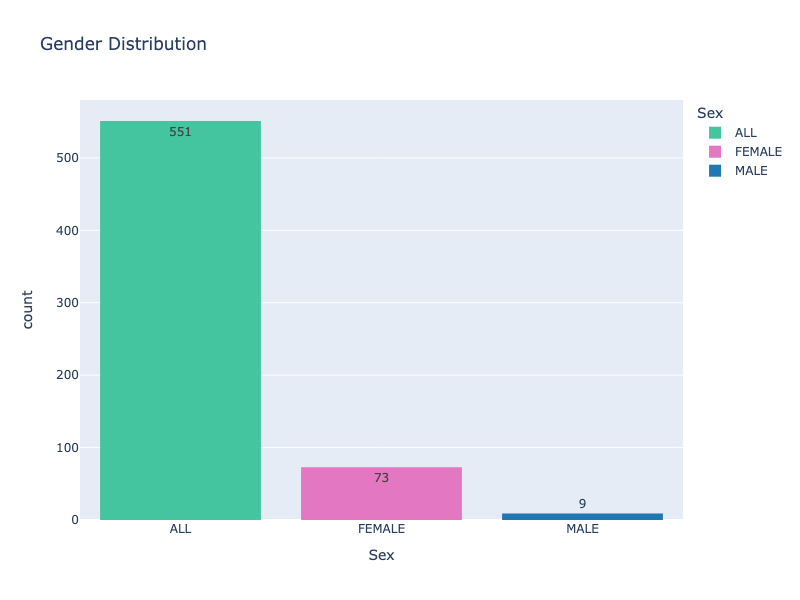
Obesity is a complex chronic condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. There are several methods available for managing obesity, including lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical interventions. While these treatments can be effective, they are not without potential side effects. Understanding the risks and benefits of each treatment option is crucial for individuals and healthcare providers when making informed decisions about obesity management.

Morbid obesity, also known as Class III obesity, is a severe form of obesity with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher. It significantly increases the risk of developing life-threatening health conditions and can greatly impact life expectancy. Numerous studies show that morbid obesity is associated with a reduction in life expectancy due to its connection with chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
Morbid obesity, also known as Class III obesity, is a severe form of obesity characterized by an excessively high body mass index (BMI) that significantly increases the risk of developing serious health complications and life-threatening diseases. It is the most extreme category of obesity, requiring more intensive treatment and management due to its associated health risks.
Obesity and morbid obesity are both medical conditions related to excessive body weight, but they differ in terms of severity, associated health risks, and treatment approaches. While obesity is a serious condition that increases the risk of several chronic diseases, morbid obesity is an even more extreme form, with higher risks of life-threatening complications. Understanding the differences between obesity and morbid obesity can help individuals and healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment strategies for long-term health.
Bariatric surgery is a highly effective treatment for individuals with severe obesity (Class III obesity or a BMI of 40 or higher) and those with a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes or heart disease. This surgical intervention is not just about weight loss; it’s about improving overall health, reducing the risk of life-threatening diseases, and enhancing the quality of life.
Obesity is a complex, chronic medical condition characterized by an excessive amount of body fat. It results from a combination of multiple factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. While the root cause of obesity is an energy imbalance—consuming more calories than the body uses—many underlying factors contribute to this imbalance. Here’s a breakdown of the common causes of obesity, including the role of genetics, diet, physical activity, and other influencing factors.